Measures for reducing global warming
We are working hard to promote energy conservation and reduce the emission of CO2, a major factor in global warming
Installing photovoltaic generation systems for our own consumption

Photovoltaic panels on the main administrative building at Wako
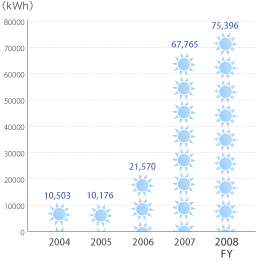
In FY 2008, photovoltaic generation panels with an output of 30 kW were installed on the roof of the main administrative building on the Wako campus. This is third installation of such panels at Wako, following those installed on the Nishina Lodge rooftop, and generates power for the air conditioning of the ground floor of the administrative building. The nursery building at the Yokohama Institute and the XFEL building at Harima also have such solar generators. Installation is planned for the Next-generation Supercomputer facility in Kobe and elsewhere. The overall power generated in RIKEN by the photovoltaic panels was 75,396kWh in FY 2008 and the total is expected to increase in the future.
■Annual solar generated power
Upgrading facilities for more energy efficiency

LED lighting
When upgrading a facility, we make sure that energy efficiency is also improved, introducing double glazing windows and newer and greener air conditioning systems as well as installing energy consumption meters. Installation of inverters and more energy efficient lighting such as LED are also underway. Reviews were made and changes have been introduced for temperature settings and operating hours in existing facilities to further cut energy use.
In future we will continue to switch to more energy efficient systems and equipment in line with upgrading schedules.
Educating our employees

Energy awareness panel display
It is important to take physical measures such as installing photovoltaic generation systems and high efficiency equipment, but the most important goal is to instill energy awareness in the users of energy. At RIKEN we are taking various measures to raise the awareness of employees; distributing energy saving messages in printed documents and through in-house broadcasts, encouraging dress codes such as ‘Cool Biz’ and ‘Warm Biz’, including providing energy conservation related content on the internal network and setting up panel displays. Each RIKEN institute is also making its own efforts for energy conservation. For example, the Tsukuba Institute has a ‘Save Energy Patrol’ to moderate energy consumption as well as educate the staff. The Wako Institute has installed display panelsshowing the energy generated by the solar panels as well as overall energy consumptionon campus.
Individual efforts to saving energy

Energy saving power strips

Lights off at lunch break
RIKEN employees are making small but valuable contributions to energy saving by turning off room lights at lunch break, using the energy saving mode for photocopiers, turning off computers or using sleep mode when leaving the desk, making sure to turn lights whenever they are unnecessary, encouraging more climate-friendly dress codes such as ‘Cool Biz’ and ‘Warm Biz’, and using circulators to moderate room temperature. As part of this kind of organization-wide effort, the Wako Institute, following the examples set last year by the Tsukuba and Kobe campuses, installed energy savingr power strips to reduce the consumption of stand-by electricity when no one is in the office.
Reducing CO2 with CGS and MGT power facilities

Cogeneration system at the Wako campus
Following the installation of a gas turbine cogeneration (CGS) plant in the RIBF building on the Wako campus in 2003, a micro gas turbine (MGT) plant was installed at the Yokohama Institute when the main office building was extended in May 2007. These plants contribute significantly to reducing CO2 by recovering and utilizing heat from power generation.
A cogeneration plant was also introduced in the common use area of the Kobe MI R&D center, where RIKEN’s Molecular Imaging Program is situated. Sharing the cogeneration plant among all the resident organizations in the building is another way of reducing CO2.
Another CGS plant is being built at the Next-generation Supercomputer facility and is expected to be completed in 2010. This CGS plant will enable power generation as well as the efficient use of otherwise wasted heat, and will further reduce RIKEN’s overall CO2 emission, contributing to reducing the environmental impact of RIKEN’s activities.