|
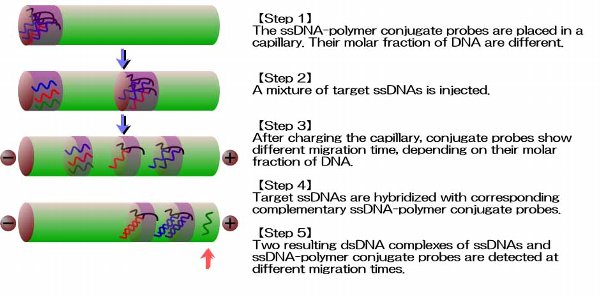
A novel concept for separating multiple targets, a probe-regulated
simultaneous separation (PRESS), was successfully developed using capillary
electrophoresis. PRESS methodology is based on the fact that target genes
were hybridized with corresponding probes, and resulting complexes were
detected at different migration times. We found that the electrophoretic
mobility of DNA-grafted conjugate-probes were different, depending on their
molar fraction of DNA. We successfully separated two target DNAs having the
same chain length using two DNA-grafted conjugate-probes.
|
|
|
Novel gene assay
methodology using affinity bioprobes
|
|
