j_h÷ó×Eɨ¯éI^C^[tFY¶§ä@\
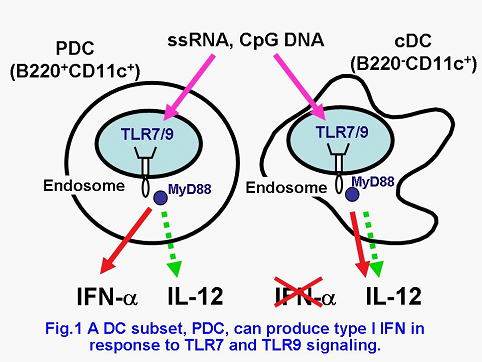
TLRs are able to recognize a variety of immune adjuvants. These adjuvants can be categorized into lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids according to their molecular characteristics. TLRs are able to transduce common immunostimulatory signals, but each TLR is also able to exhibit its own function. We are attempting to clarify how TLRs exert their pleiotropic functions, especially on DCs. Notably, nucleic acid adjuvants are featured by their ability to induce type I interferons(IFNs), especially IFN-alpha. Single stranded RNA (ssRNA) and CpG DNA function as the ligands for TLR7 and TLR9, respectively. TLR7- and TLR9-induced IFN-alpha production depends on a DC subset, called as plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDCs) (Fig.1). PDC can be distinguished from conventional DC (cDC) according to the surface molecule expression. PDC expresses only TLR7 and TLR9 among TLRs and, by sensing virus-derived nucleic acids, plays vital roles in antiviral immunity as a type I IFN producing cell.
Nucleic acid-induced type I IFN production also contributes to the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In those patients, anti-nucleic acid Abs are generated and form complexes with host-derived nucleic acids. Those complexes can induce type I IFNs. Indeed, in the patients, serum type I IFN levels are elevated and the elevation is correlated with the severity of the diseases.
All TLR7/9-mediated effects, inlcluding induction of both inflammatory cytokines and type I IFNs, are dependent on a TLR-associated cytoplasmic adapter, MyD88. Downstream of MyD88, the signaling pathway is bifurcated into two pathways for inflammatory cytokine and type I IFN induction. The former pathway depends on NF-kappaB and the latter pathway, specific for PDC, requires a transcription factor, IRF-7.
We have identified IKKalpha as a critical kinase selectively involved in
this We have identified IKKalpha as a critical kinase selectively involved
in this PDC-specific pathway (Fig.2). In IKKalpha-deficient mice, ability
of PDC to produce IFN-alpha in response to TLR7/9 signaling is severely
impaired. However, TLR7/9-induced production of inflammatory cytokines
is mildly or marginally impaired. IKKalpha can associate with and phosphorylate
IRF-7, thereby activating IRF-7 function. IKKalpha should be a candidate
target molecule for treating autoimmune disorders.

